WHAT WE DO

INNOVATIVE PROJECTS (www.siav.net)
/6CEBAB5EF888C91DC12575630038593C/$file/blocco_innovazione.gif?openelement) |
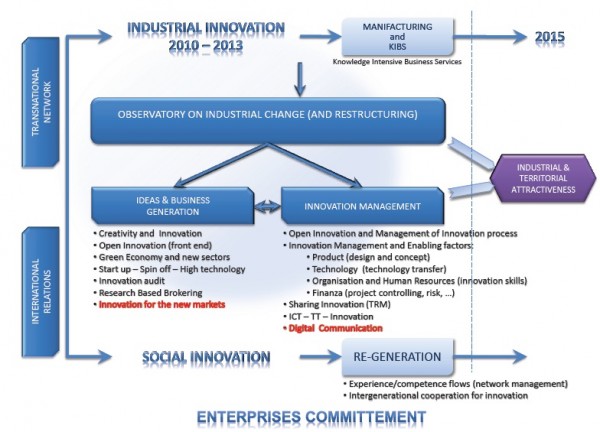
“Industrial Change” is the process which allows a productive sector to react to the evolution of the economical context and ensure competitiveness and continuous growth opportunities. Unlike “Restructuring”, it does not present any discontinuity feature, as it anticipates trends through competitors evaluation and markets evolution’s analysis. A part from public-funded support, the essential factors to overcome the problems aroused from industrial change are considered to be the Development of New Technologies and the qualification of Human Resources to be implemented through a flexible approach and with all the tools necessary to adapt to different criticalities at structural, economical and geographical level. |
/2DAB94C1BDA59A5CC1257563003924D1/$file/blocco_skill.gif?openelement) |
Innovation represents the key for competitiveness, essential factor for the development of enterprises and employment. It is based on the capacity to implement changes and manage it over time. Change shall therefore become an opportunity for business. Innovation is something more than a “good idea”, it is a mix of ideas proposed by a motivated staff able to fulfill market’s expectations. Innovation requires the organization of a an “enabling track” based on a strategy, a development of relations among functions and people, a structuring of an adequate and innovative organizational context, an acquisition of knowledge and competences suitable for its management. The financial investment to innovate may result a burden for small enterprises, therefore cooperation frameworks shall be foreseen to reduce costs and risks, to create economies of scale, reduce realization times and promote shared learning structures. |
/E4485153E75725C0C12575630039339E/$file/blocco_metodo.gif?openelement) |
Until nowadays Vocational Training has been organized according to two main approaches: “intentional” (or Formal Learning), planned and organized to develop learning and “implicit” (or non-formal learning) as a result of activities not organized on purpose (e.g. work). Today a third approach, defined “context-based”, is applied to on-the-job practices structured to develop learning during, within and through work experiences. It encompasses research-intervention initiatives, improvement projects, action learning, plans and actions from development. This is the shift from a teacher-based method and programme to a track built and shared with the participant, in order to connect new knowledge to prior learning, knowledge and systems already integrated and active in her/his working and everyday life. An organization nowadays survives and competes according to its ability to identify, acquire and apply competences, avoiding on the one hand the risk of overload and considering the necessity for keeping useful competences (“core competencies”) and on the other outlining the essential processes for knowledge transfer and knowledge development; as pointed out by Anthony G. Oettinger “How much tradition to avoid death and how much innovation to avoid outburst?” |
/038F6637577C53D6C125756300393838/$file/blocco_altri.gif?openelement) |
Ageing of the workforce is an European priority issue. Late retirement is only one of the answers to the aged people growth impact on the socio-economic system, it will need specific measures in order to enable: employers to foresee active management of older workers, employees to acknowledge the need to work longer. Demographic change in Veneto is similar to other EU regions, nevertheless, despite an increase of the aged workers number from 1998, there is one of the lowest Italian rate of active aged workers. Moreover, Italy itself is at the bottom of the EU positioning chart.
Upon these facts, initiatives and activities carried out by Confindustria Veneto SIAV in the last years focused on age management problems within companies. New human resources strategies have been designed and introduced, testing skill transfer methodologies and fostering intergenerational dialogue.
Some efforts have been done in the Age management field in the framework of community and regional programmes as well (EQUAL, Leonardo da Vinci, FSE, Grundtvig), involving more than 600 companies in the following topics:
– Exploitation and transfer of skills
– Intergenerational cooperation
– Active ageing. |



/6CEBAB5EF888C91DC12575630038593C/$file/blocco_innovazione.gif?openelement)
/2DAB94C1BDA59A5CC1257563003924D1/$file/blocco_skill.gif?openelement)
/E4485153E75725C0C12575630039339E/$file/blocco_metodo.gif?openelement)
/038F6637577C53D6C125756300393838/$file/blocco_altri.gif?openelement)


